How Sunrun Improved Safety, Cutting Incidents 18%
My Role:
LXD – End-to-End
Audience:
Field Safety Employees
Duration:
10 months
Tools:
Articulate 360 Rise | Figma | Simpplr (Current) | Docebo (LMS) | Premiere Pro | Mural | Asana
OVERVIEW
Sunrun, a national leader in residential solar energy, employs over 10,000 workers—many of whom perform high-risk jobs on rooftops and around electrical systems. As the company scaled, so did the complexity of keeping everyone safe.
With evolving OSHA regulations and a geographically dispersed workforce, the Safety Team recognized that outdated training materials and inconsistent practices were no longer sufficient.
The Challenge
Several gaps threatened both compliance and field safety:
- Legacy training material were outdated and inconsistent across regions.
- OSHA regulations had evolved, but internal content hadn’t.
- Employees lacked confidence in handling complex or high-risk scenarios.
- Engagement with static, text-heavy training was low.
The stakes were high: a misstep on a rooftop could mean a life-threatening fall or electrical hazard.
The Safety team set ambitious goals to close the compliance gap and improve safety outcomes across the board.
Goals
To course-correct, Safety Team set clear targets:
Deliver a scalable safety training plan for 3,000+ field employees
Build crew confidence and increase safety adherence
Improve field safety metrics and ensure OSHA compliance
Reduce high-severity incidents on job sites
The Solution
To improve safety outcomes, we launched a comprehensive training overhaul targeting a specific date rollout. In collaboration with Safety Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) and department leaders, we created scenario-based, mobile-friendly content designed for real-world application in the field.
Key deliverables included:
10 Current microlearning modules with built-in quizzes and 2 interactive eLearnings
Updated and rewritten for clarity, compliance, and alignment with current safety practices
Scripted and filmed on active job sites to simulate real hazards like ladder falls, rooftop navigation, and electrical risks
* Current: An intranet hub for personalized, role-based updates—keeps employees informed and engaged.
Microlearning (Current)
Click play to learn more.
Ladder Safety eLearning
View to discover more
To enhance engagement and retention:
🎙️ AI VoiceOver provided consistent, clear narration
🧠 Interactive features such as drag-and-drop, multiple choice, and decision points were embedded to promote active learning and situational thinking
All content was deployed in a modern, mobile-friendly LMS with tracking capabilities to ensure visibility and compliance across teams.
My Process
With the end goal in mind, I worked through the ADDIE model to create an experience that would resonate with the learner by connecting to past experiences, highlighting immediate job relevance, and focusing on a problem/solution format.
* While the content itself was proprietary, the process behind the transformation was structured, collaborative, and deliberate.
My Role
I led the end-to-end learning experience design, owning every phase from needs assessment through implementation. My focus was on creating a field-first, compliance-aligned safety training program that was scalable, relevant, and effective.
Stakeholder Collaboration
To ensure cross-functional alignment and impact, I partnered with key teams across the organization:
Safety SMEs & Leaders – Collaborated with national and regional safety leads, safety managers, and both warehouse and field employees to identify high-risk scenarios and real-world challenges.
LMS Administration (Docebo) – Worked closely with the LMS administrator to manage system configuration, assign training paths, track completions, and generate compliance reports. All training was SCORM-compliant and integrated with Docebo’s analytics tools.
Legal & Compliance – Ensured training content aligned with OSHA standards, internal safety policies, and SOPs—critical not only for safety compliance but for broader company-wide adherence.
Communications Team – Coordinated course launch messaging to drive awareness, ensuring the right teams received timely and relevant information.
Discovery
The project kicked off with stakeholder interviews and a comprehensive audit of existing training content using the GROW framework (Goal, Reality, Options, Way Forward). This helped identify gaps, validate needs, and prioritize content development.
Key Inputs Came From:
Safety SMEs & Department Leads – Shared frontline risks, common safety violations, and areas where knowledge gaps impacted performance.
Legal & Compliance Partners – Helped define training requirements tied to regulatory standards.
Field Teams – Provided direct insight into learner pain points, engagement blockers, and how to make training more usable and realistic on the job.
The project began with in-depth stakeholder interviews and a thorough audit of existing training, using the GROW model framework to guide analysis. Input was gathered from:
Safety SMEs and Department Leads – to surface real risk scenarios and priority hazards
Legal and Compliance Teams – to align training with OSHA and internal regulatory requirements
Field Teams – to ensure the content would be relevant, practical, and resonate with those on the job

Content Strategy & Development
I recognized early that to build something meaningful, I needed to understand the learner’s environment. So I:
- Shadowed field crews on-site to observe workflows, identify learning gaps, and ask directly about training pain points.
- Learned that previous courses were outdated, non-interactive, too long, and disconnected from daily safety needs.
- Discovered key friction points:
- Video content was irrelevant or old
- Courses were not translated or language-accessible
- Safety protocols had evolved, but the training hadn’t
In response, I partnered with SMEs to:
- Update or replace outdated videos using real job scenarios and safety scripts.
- Prioritize courses (narrowing 22 down to 12) based on OSHA requirements and field relevance.
- Ensure all content was translated and accessible.
- Build a common foundation for safety that every field role could rely on—then customize where needed.

I recognized early that to build something meaningful, I needed to understand the learner’s environment. So I:
- Shadowed field crews on-site to observe workflows, identify learning gaps, and ask directly about training pain points.
- Learned that previous courses were outdated, non-interactive, too long, and disconnected from daily safety needs.
- Discovered key friction points:
- Video content was irrelevant or old
- Courses were not translated or language-accessible
- Safety protocols had evolved, but the training hadn’t
In response, I partnered with SMEs to:
- Update or replace outdated videos using real job scenarios and safety scripts.
- Prioritize courses (narrowing 22 down to 12) based on OSHA requirements and field relevance.
- Ensure all content was translated and accessible.
- Build a common foundation for safety that every field role could rely on—then customize where needed.
Design Decisions and Outcomes
To modernize onboarding and compliance training, we built a scalable, field-first learning strategy rooted in real-world scenarios and powered by smart content delivery that included:
Scenario-Based Learning Objectives:
We created eLearnings that mirrored real job-site risks, increasing relevancy and retention. These modules contributed to a 10% increase in training completion rates, driven by learners recognizing real-world value.
Multilingual Accessibility:
We offered content in preferred languages, addressing one of the most reported barriers during job shadowing. This boosted comprehension and engagement, especially among Spanish-speaking field teams.
Blended Delivery Format:
A mix of microlearnings, interactive quizzes, and real-world video simulations helped improve knowledge checks and application. Quizzes required 100% accuracy on critical safety topics, directly supporting OSHA compliance goals.
Modular, AI-Enhanced Content Design:
Content was structured for digestibility, flexibility, and intelligent updates. Using AI tools, we tracked learner behavior to suggest next steps, which helped reduce course abandonment and supported just-in-time learning—key for improving day-to-day safety behaviors in the field.
The Before
Content drafts, Course Outlines, Script Development, and Behavior Mapping




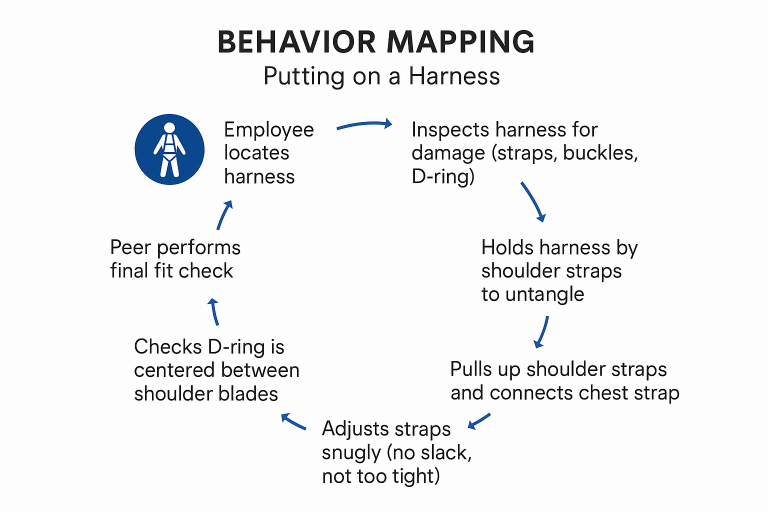
Implement
The implementation rolled out in carefully phased stages:
Months 1-2
Planning and stakeholder audits
Months 3-6
Content production and testing
Months 7-8
LMS integration and pilot rollout
Months 9-10
Launch and monitoring
Training was deployed via the company’s LMS, making it trackable and fully OSHA-compliant. Pilots with select field teams provided early feedback that refined final content.
Weekly standups, shared timelines, and real-time feedback loops ensured transparency and momentum.
Results
The project was evaluated using both qualitative and quantitative measures:
⚠️ Noticeable drop in severe safety incidents and OSHA violations
🧠 Increased crew confidence and improved engagement with safety protocols
🔒 Full integration into a compliant LMS, ensuring version control and data tracking
Success driver: Strong collaboration and alignment with field operations
These efforts led to an 18% improvement in our DART rate (Days Away, Restricted or Transferred) rate year over year—further proof that a strong safety culture drives strong business outcomes.
Safety Training Completion (Safety Dept.):
- Completion rates rose from 80% to over 90%, a direct result of training that felt useful, human, and credible.
- Fewer safety violations were reported in the 3 months post-training.
- OSHA compliance audit scores improved year-over-year.
Impact Statements from the Safety Team Members
“We’ve had fewer injuries and more team members speaking up when they see something unsafe.”
“We used to rely on experience—now we rely on training and experience. That’s a big shift.”
Quotes from the Field
“The training is real-world and easy to follow. It’s not just a policy—it’s about going home safe every day.” – Crew Lead

Conclusion
This project confirmed that real-world, scenario-driven training can drive measurable improvements in safety outcomes. Applying a structured framework ensured that each stage—from design to evaluation—was intentional and effective.
Key Takeaway:
One of the most valuable lessons was the importance of adaptability and collaboration. Despite delays, shifting priorities, and even lost footage, the team remained resilient by pivoting quickly and staying aligned.
Once the SMEs recognized the training’s value, their engagement increased significantly—underscoring the importance of early buy-in and shared vision.
What to Improve:
To build on this success, we identified key areas for refinement:
Accelerate Timelines: Projects took longer than expected. Establishing leaner processes and milestone tracking can help improve turnaround.
Proactive Industry Tracking: We missed some updates—building a rhythm for regular check-ins with Compliance will keep content relevant.
Clarify Roles Early: Misalignment in the early stages caused delays. Setting clear responsibilities and expectations upfront will save time.
Empower SMEs: Some hesitated to make decisions. Ongoing support and clarity around decision-making authority will build SME confidence and accountability.
Forward Strategy:
To work smarter in future initiatives:
Implement pre-kickoff alignment sessions with stakeholders to define goals, roles, and timelines.
Build in feedback loops and checkpoints to adjust swiftly when priorities shift.
Maintain a shared asset library and backup system to avoid disruptions due to lost materials.
Create a SME onboarding guide to clarify their role in training development and safety decision-making.
By learning from this experience and applying these strategies, we can continue modernizing training in a way that is faster, smarter, and even more impactful.
How it all Began...
Looking to work on and get more experience on a design team, I saw a posting by a group member, which piqued my interest, to work on a Hackathon (Climate Change App Challenge) for monday.com and their users.
The project itself was to build an app that can help teams and organizations take an active role in combating climate change.
The group of volunteers consisted of 10+ like-minded people located around the world with various disciplinary backgrounds who shared a common interest in design and technology
We first had to decide on a topic that would appeal to users and we decided on Reducing Carbon Emissions with Everyday Tasks.
Individuals were grouped to tackle various tasks for the initial research: competitive analysis, surveys, and interviews to gather more information for the project.

